Abstract
Background: Pyruvate kinase (PK) deficiency is a rare hereditary chronic hemolytic anemia caused by PKLR gene mutations. Clinical management includes regular red blood cell (RBC) transfusions; some children require splenectomy, which carries a risk of sepsis and thrombosis. PK deficiency is associated with serious complications, regardless of transfusion status. There are no approved pharmacotherapies in children and there is a global unmet need for therapies targeting the underlying cause of hemolysis. Mitapivat (AG-348), an oral, allosteric activator of the RBC PK enzyme, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of hemolytic anemia in adults with PK deficiency. In the ACTIVATE-T (NCT03559699) phase 3, open-label study, mitapivat demonstrated significant reduction in transfusion burden in adults with PK deficiency who are regularly transfused; 37% achieved a transfusion reduction response and 22% achieved a durable transfusion-free status that was maintained in the long-term extension study (NCT03853798). Safety and efficacy data support the evaluation of mitapivat in children with PK deficiency who are regularly transfused. Here, we report the design of the phase 3 ACTIVATE-KidsT study (NCT05144256), which will evaluate the efficacy and safety of mitapivat in children with PK deficiency who are regularly transfused.
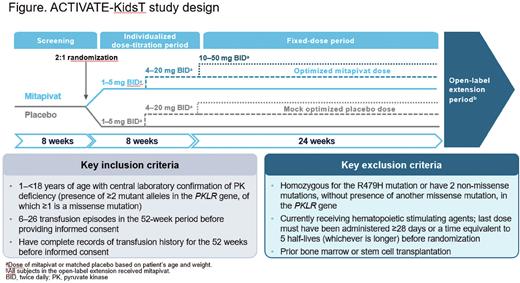
Methods: ACTIVATE-KidsT, a phase 3, global, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, will stratify 45 children by age and splenectomy status. A minimum of 6 patients per age group (1-<6, 6-<12, and 12-<18 years) will be randomized (2:1) to receive mitapivat or placebo (Figure). The double-blind portion includes an 8-week (wk) dose titration period and a 24-wk fixed-dose period; a 5-year open-label extension (OLE) will follow. Study drug will be administered orally (as granules taken with food or tablets swallowed whole) at a dose of 1-50 mg twice daily, depending on age and weight. Pediatric dosing is based on pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation such that, within each age and weight category, the proposed dose provides exposure similar to that in adults at the same dose level. To gradually increase hemoglobin levels, study drug dose level will be sequentially increased during the dose titration period, with dose level increases occurring approximately every 4 wks. Key inclusion criteria include: ≥2 mutant PKLR alleles with ≥1 missense mutation; ≥6 transfusion episodes in the past year. Key exclusion criteria include: R479H homozygosity; presence of 2 non-missense mutations in PKLR without a missense mutation; or prior stem cell transplantation. The primary endpoint is transfusion reduction response (TRR), defined as ≥33% reduction in transfusion volume during the fixed-dose period normalized by weight and actual study drug duration, compared with historical transfusion volume standardized by weight and to 24 wks. Secondary endpoints will assess the effect of mitapivat on transfusion-free status, iron metabolism and overload, safety, quality of life, and pharmacokinetics. With a planned sample size of 45 randomized patients (mitapivat, N=30; placebo, N=15), and assuming a TRR rate of 35% for mitapivat and 5% for placebo, there will be >80% probability that the lower bound of the 95% credible interval for the odds ratio of TRR rate (mitapivat vs placebo), based on the Bayesian logistic regression model with weight ≥0.1 of a robust prior, will be >1. Analysis of the primary endpoint, TRR, will use a Bayesian logistic regression model, including TRR status (yes, no), as the dependent variable and treatment arm as the independent variable, adjusting for splenectomy status. Patients completing the double-blind period will be eligible to receive mitapivat for up to 5 years in an OLE period. During the OLE, all patients will receive mitapivat.
Results: Global site recruitment is in progress, with a total of 27 sites planned in Czech Republic, Denmark, Germany, Italy, Netherlands, Spain, Switzerland, Turkey, United Kingdom, and United States. Patient enrollment has also begun, with the first patient enrolled in July 2022.
Conclusion: The ACTIVATE-KidsT study of children with PK deficiency who are regularly transfused will evaluate the efficacy and safety of mitapivat, a potential disease modifying pharmacotherapy that targets the underlying enzymatic defect of PK deficiency.
Disclosures
Grace:Novartis: Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy; Sobi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Agios Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding. Tyler:Agios: Current Employment, Other: Stockholder. Little:Agios: Current Employment, Other: Stockholder. Kosinski:Agios: Consultancy, Other: Shareholder. Beynon:Agios: Current Employment, Other: Stockholder.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.